Basic concepts / SMS network entities
SMS messages are created by mobile phones or other devices (e.g.: personal computers). These devices can send and receive SMS messages by communicating with the GSM network. All of these devices have at least one MSISDN number. They are called Short Messaging Entities. To understand their roles in the GSM SMS network, please take a look at sms architecture diagram (Figure 1) below:
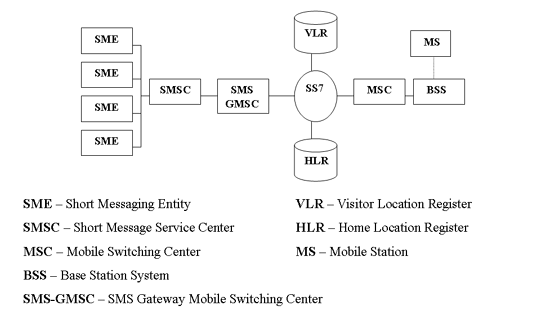
The SMEs are the starting points (the source) and the end points (the receiver) for SMS messages. They always communicate with a Short Message Service Centre (SMSC) and never communicate directly with each other. An SME can be a mobile telephone. Depending on the role of the mobile phone in the communication, there are two kinds of SMS messages: Mobile-originated (MO) messages and Mobile-terminated (MT) messages. MO messages are sent by the mobile phone to the SMSC. Mobile-terminated messages are received by the mobile phone. The two messages are encoded differently during transmission.
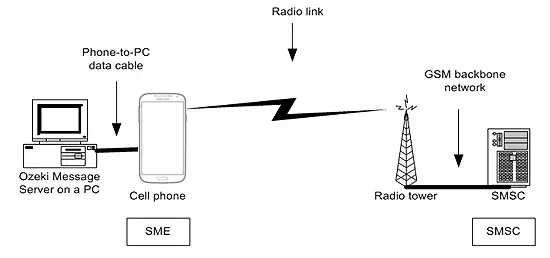
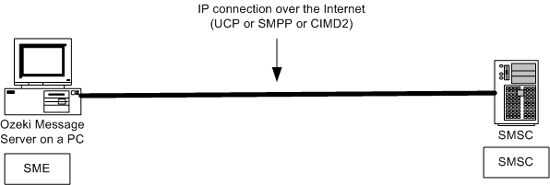
An SME can also be a computer equipped with a messaging software, such as Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway, which can communicate directly with the SMSC of the service provider. For this communication, a mobile phone attached to the PC with a phone-to-pc data cable (Figure 2) or a direct IP link (Figure 3) can be used.