Building an Ozeki NG SMS Gateway cluster
This guide gives information about how to build an Ozeki NG SMS Gateway cluster to have a redundant SMS system. Clustering can be used to increase performance or to be prepared for hardware failures. In this text a failover cluster is discussed which can be used to prepare for hardware failures. If you setup a failover cluster your system will provide better uptimes and better tolerance against hardware related errors.
Update: If you provide SMPP SMS Service, we recommend you to use the SMPP Server and SMPP Client implementations offered by Ozeki 10 SMS gateway, with Ozeki Cluster over Ozeki NG, because they provide higher message throughput.
Before we begin the configuration of Ozeki NG cluster using Microsoft Windows Server 2003, I will show you our own Ozeki Cluster software product which allows you to setup a cluster configuration easier than using Microsoft's solution.
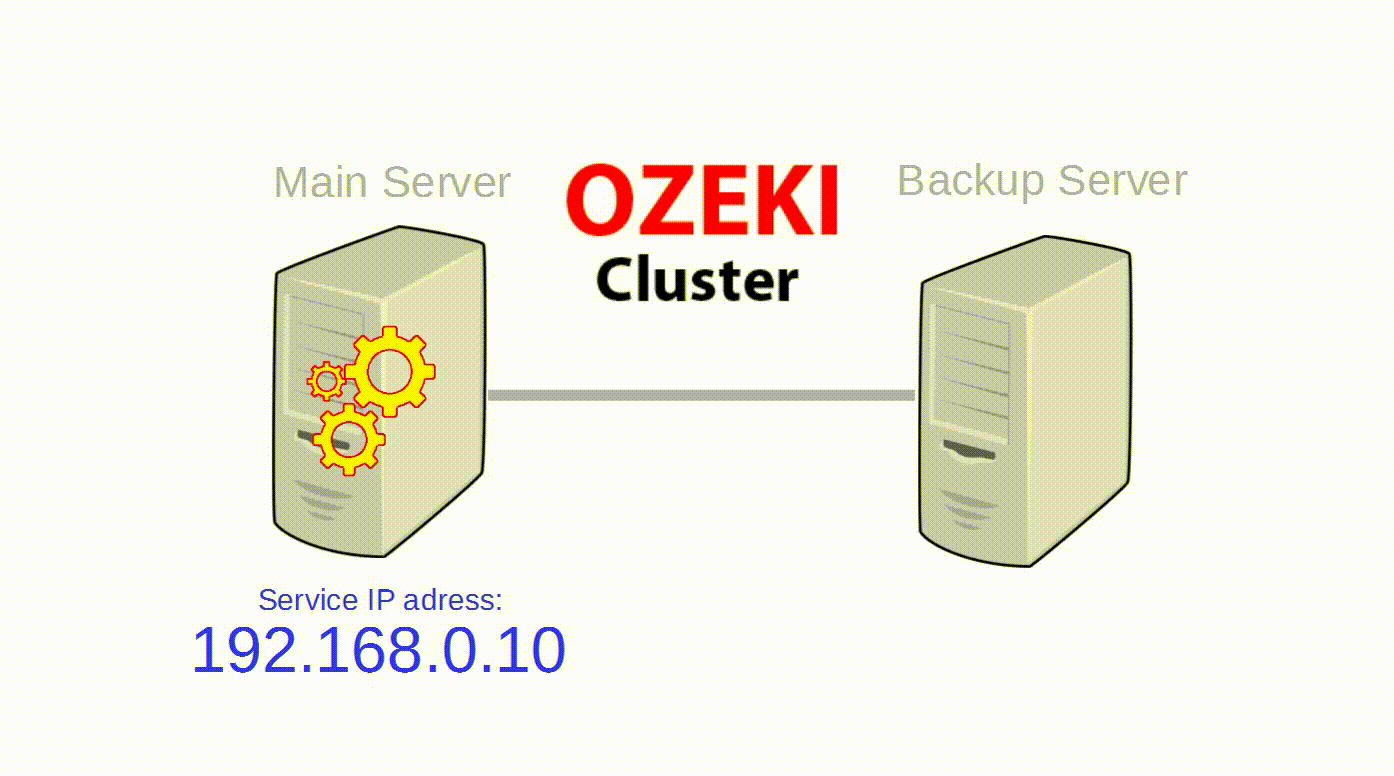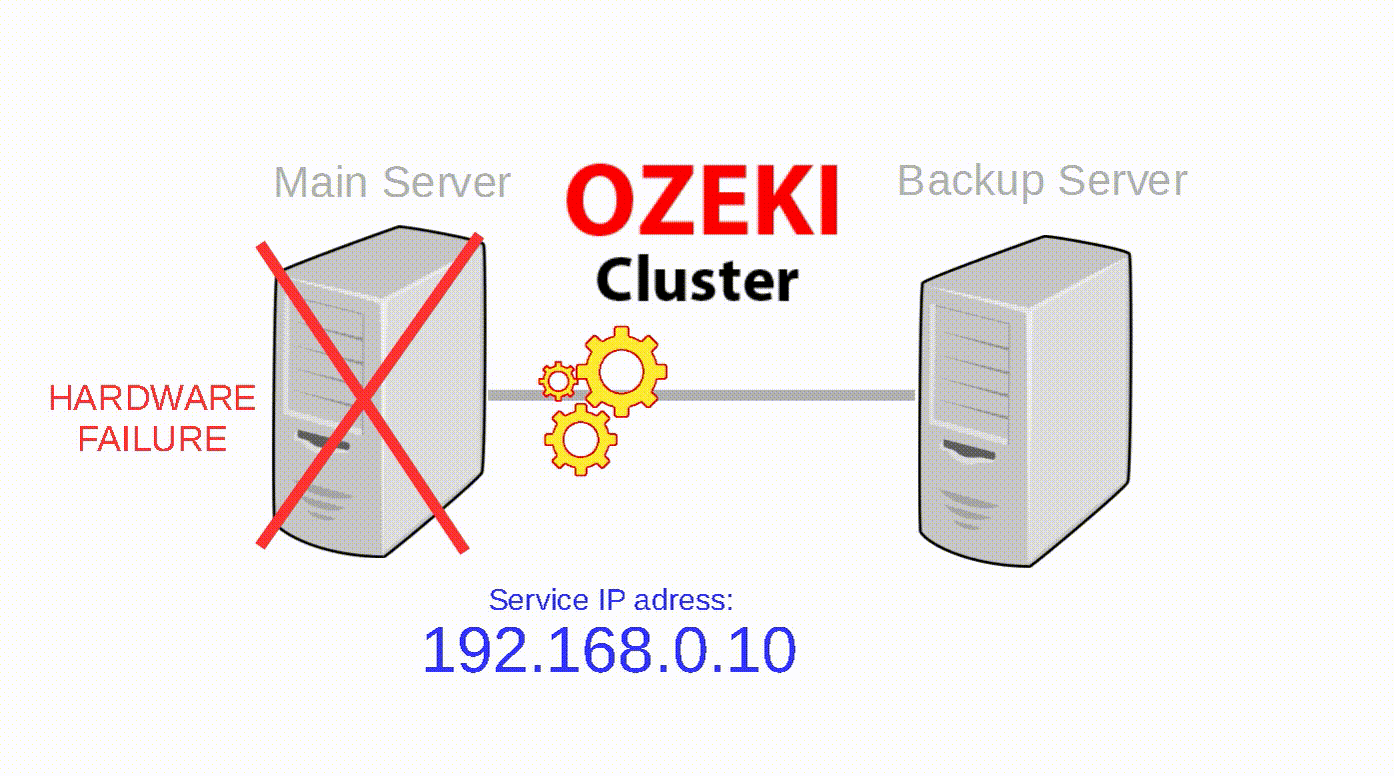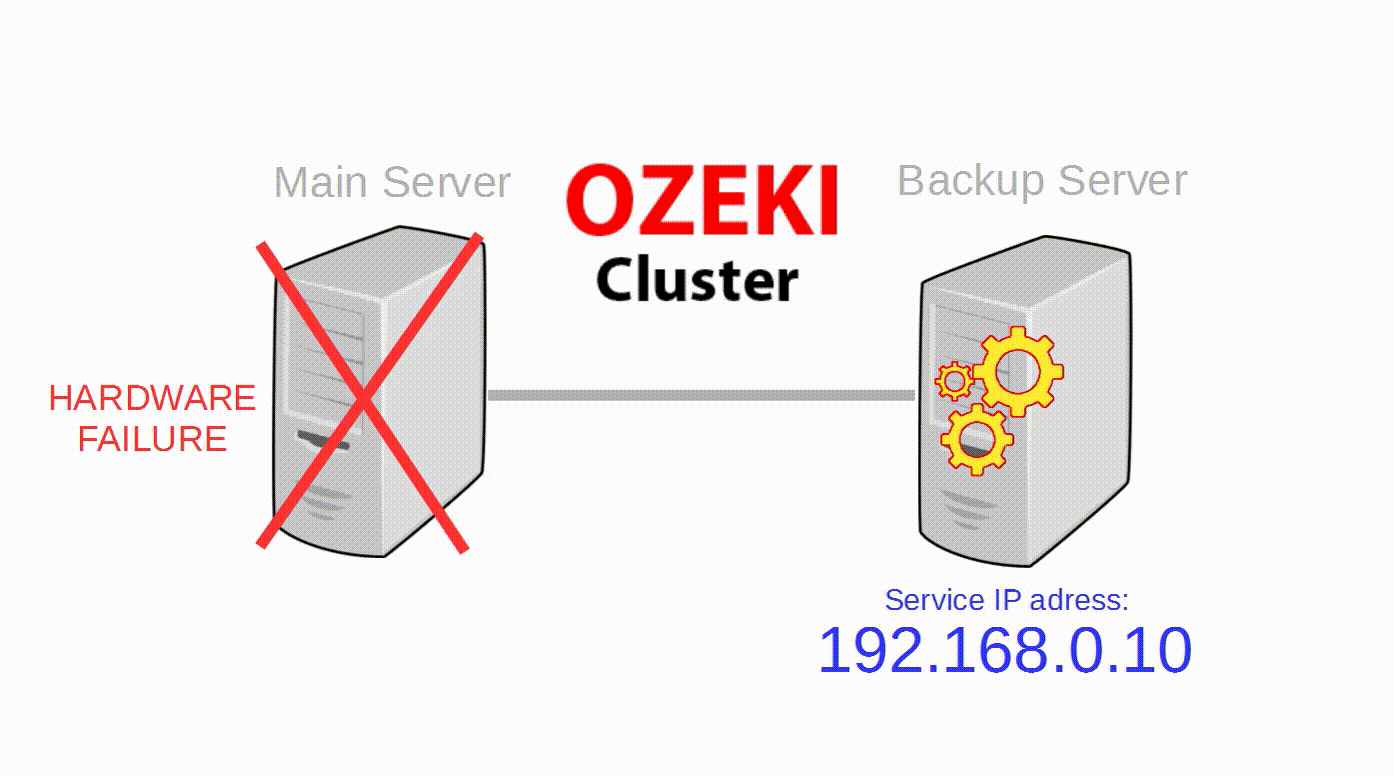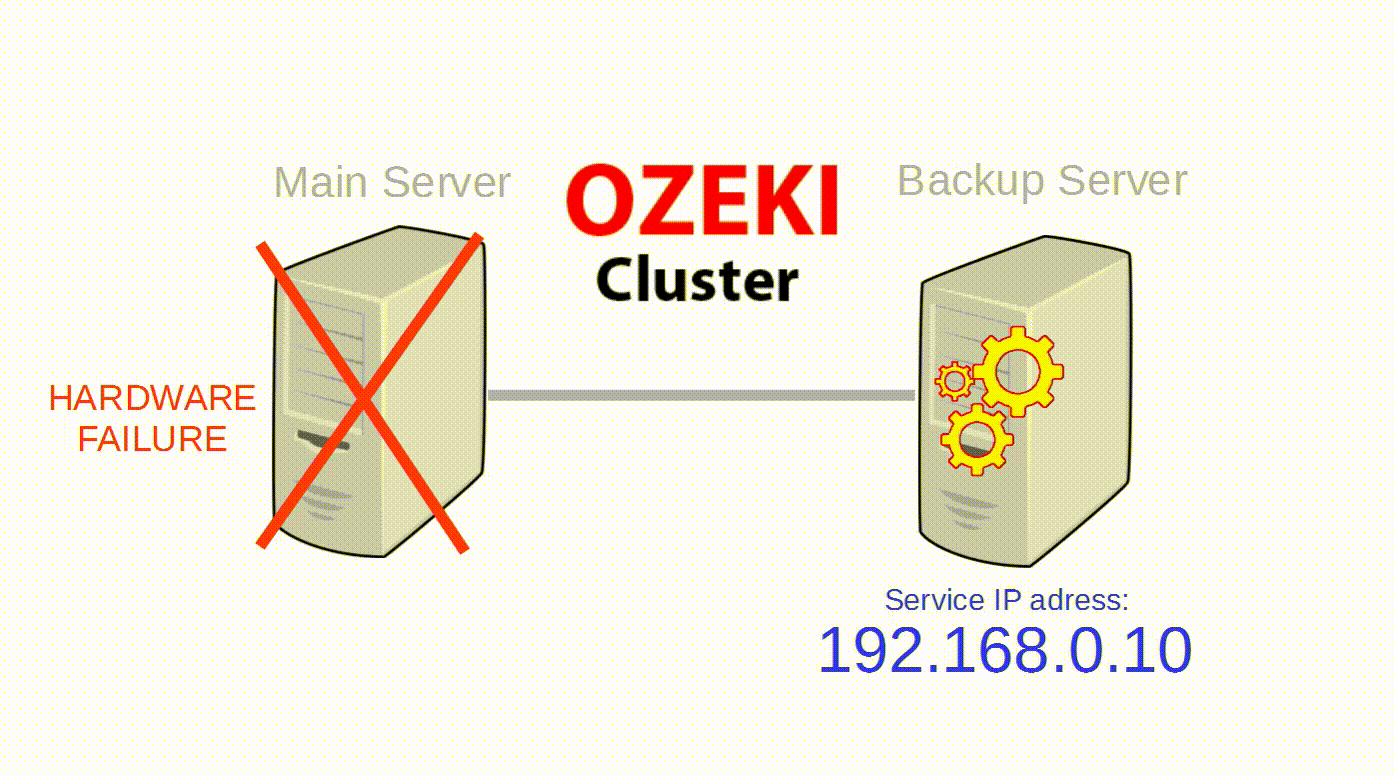
Ozeki Cluster is responsible for protecting your service against hardware failure and reach higher availability of your Ozeki NG SMS Gateway software. Ozeki Cluster automatically moves any service to another computer in case of a hardware failure. You can download it from the following website: Ozeki Cluster
In the following part of this guide you will show how to configure your Windows Server 2012 R2.
Prerequisites
To setup clustering Ozeki NG SMS Gateway should be installed on Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition or Windows Server 2008. Clustering is based on Microsoft Cluster Server technology, so concerning hardware, please refer to the Microsoft Cluster Server Administrator's Guide for a list of supported hardware configurations and hardware configuration information. In brief you will need hardware, that provides shared storage facility, and at least two physical computers that will form Node 1 and Node 2 of the cluster (Figure 1).
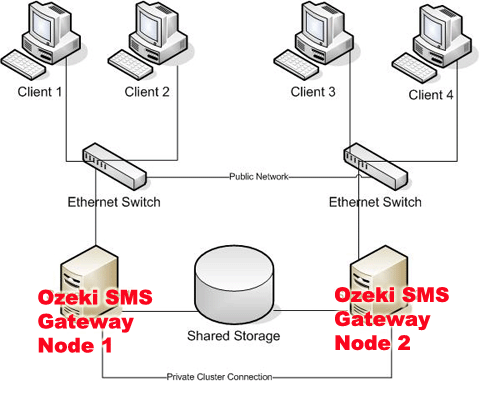
Introduction
Unlike other clusters which are made for better performance, Ozeki NG SMS Gateway
clusters are used to increase availability. The goal of a highly available system
is to provide continuous SMS service, regardless of planned or unplanned
interruption. High-Availability refers to a system uptime that approaches 100%.
For example, an availability level of 99.999%, calculated on a round-the-clock
basis, would mean that an organization would experience at least five minutes
of unscheduled downtime per year on its Ozeki SMS gateway platform. A level
of 99.99% translates to 52 minutes of downtime. A level of 99.9% translates
to 8.7 hours, and a level of 99% equals about 3.7 days of downtime per year.
The need for high-availability is not limited
to 365x24x7 environments. In many cases an Ozeki NG SMS Gateway system must be
available during normal business hours or for a critical time periods throughout
the day. A system failure during these critical periods is unacceptable for
many organizations.
An Ozeki NG SMS Gateway cluster is based on the Microsoft Cluster Server
technology. It only presents the option of failover clustering, which means
that if a failure occurs on a server that is a member of the cluster (on Ozeki
NG SMS Gateway Node 1 or Ozeki NG SMS Gateway Node 2) the SMS service that
the failing server was hosting will automatically restart itself on another
server that is a member of the same cluster. The process of a service moving
from one server to another is called Failover.
Definitions
The Ozeki NG SMS Gateway service that the cluster runs uses resources of the cluster nodes. The SMS service running on the cluster has its own Harddrive assigned to it (which is shared with the other failover cluster nodes), it has its own IP Address and it has its own Network name. All of the resources that a clustered Ozeki NG SMS Gateway service uses are called a Resource Group. The Resource group contains the basic resources that the Ozeki NG SMS Gateway service needs, Disk Drive, IP Address, and the service itself. All of these together form a virtual server that can be moved from one server to another in a matter of seconds (Failover) without any dependence on a specific server. The user that accesses this virtual Ozeki NG SMS Gateway server will be exposed to it like to any other Ozeki NG SMS Gateway installation.
Shared storage
To setup a fault tolerant Ozeki NG SMS Gateway cluster, the first thing to do,
is to build a shared storage facility. This facility should have a disk subsystem
that uses RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks).
RAID refers to the grouping of individual hard disks in a way that provides
continued operation in the event of a disk failure. The shared storage you
setup for an Ozeki NG SMS Gateway cluster can be both hardware RAID (e.g., a
RAID controller is used) and software RAID (e.g., the functionality is provided
by an operating system or application). There are many forms (levels) of RAID:
- RAID-0: Stripe set without parity. Stripe sets work well with databases due to the usually random I/O nature of database transactions. In RAID-0, data is divided into blocks and spread (in a fixed order) across all of the disks in an array. RAID-0 improves read/write performance by spreading operations across multiple disks, so that operations can be performed independently and simultaneously. While RAID-0 provides the highest performance, it does not provide any fault tolerance. If a drive in a RAID-0 array fails, all of the data within the stripe set becomes inaccessible.
- RAID-1: Mirroring. Disk mirroring provides a redundant, identical copy of a disk. Data written to the primary disk is also written to a mirror disk. RAID-1 provides fault tolerance and generally improves read performance, but it may also degrade write performance. Because dual-write operations can degrade system performance, many mirror set implementations use duplexing, where each mirror drive has its own disk controller. While the mirror approach provides good fault tolerance, it is relatively expensive to implement. In addition, only half of the available disk space can be used for storage. The other half is needed for mirroring.
- RAID-5: Stripe set with parity. RAID-5 provides redundancy of all data on the array, allowing a single disk to fail and be replaced, in most cases, without system downtime. RAID-5 offers lower performance than RAID-0 or RAID-1 but higher reliability and faster recovery. RAID-5 uses the equivalent of one disk for storing the parity strips, but distributes the parity strips across all the drives in the array. The data and parity information are arranged on the disk array so that they are always on different disks.
There are other implementations of RAID, such as RAID-0+1 (aka RAID-10), RAID-2,
RAID-3, etc., but these are typically proprietary implementations unique to the
hardware manufacturer that support them.
When you build the shared storage facility, make sure, that all shared disks,
must be physically attached to a shared bus. Verify that disks attached to the
shared bus can be seen from all nodes. This can be checked at the host adapter
setup level. (Please refer to the manufacturer's documentation for
adapter-specific instructions.)
SCSI devices must be assigned unique SCSI identification numbers and properly
terminated, as per manufacturer's instructions. All shared disks must be
configured as basic (not dynamic). All partitions on the disks must be
formatted as NTFS.
Network connectivity
Each node of the SMS Gateway cluster should have two network adapters, one for
connection to the public network and the other for the node-to-node private
cluster network. If you use only one network adapter for both connections,
your configuration is unsupported.
Installation
During the initial installation, please make sure that you install the same
Ozeki NG software version on both nodes of the cluster. Concerning the
installation path, all files should be installed to the shared disk resource.
Installation steps:
- Install a supported Windows OS and accept the default application choices.
- After you have installed the Windows OS on the first node and before you install MSCS, click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Configure Your Server.
- Click Advanced\Cluster Service, and then in the right pane click Learn More.
- In the Windows Help menu, review item 2 in the "Windows Clustering" topic. Follow the instructions in the "Windows Clustering" topic to install MSCS. Important You must read the "Planning for Windows Clustering\Requirements" for server clusters and follow the checklist for server clusters named "Checklist: Creating a server cluster". The "Checklist: Creating a server cluster" topic is located under the "Server Clusters section\Checklist" for server clusters topic.
- After you successfully install MSCS, you must configure MSDTC to run on a cluster.
- On the Start menu, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, point to Cluster Administrator, and then click View Groups\Cluster Group. If the group contains an MSDTC resource, proceed to step 9. If the group does not contain an MSDTC resource, complete the following two steps.
- On the Start menu, click Run. In the Run dialog box, enter the command cmd and then click Ok. In the Command Prompt window, on the command line, enter: Comclust.exe
- Repeat step 7 on the remaining nodes of the cluster, one node at a time.
- Install Ozeki NG SMS Gateway on all cluster nodes.
- Activate Ozeki NG SMS Gateway on all cluster nodes.
- Declare Ozeki NG SMS Gateway as a cluster resource.
- Bring the Ozeki NG cluster resource online.
- Test the cluster functionality by opening the SMS gateway configuration GUI from a browser using the IP address of the cluster.
Additional information
One more thing to consider when you install your SMS gateway cluster is the possibility of a power outage (which could cause both nodes to restart at the same time). To ensure that both nodes of the cluster never start at the same exact time, change the Boot.ini file timeout value of one node to 10 seconds and change the value of the other node to 90 seconds. This gives one node plenty of time to "get ahead" of the other node, and prevents the computers from competing for the shared disks, which could cause a failure.
Common tasks
Shutdown: To shutdown Ozeki NG on a cluster, you need to user the "cluster.exe" command, that comes with the Windows OS. The basic syntax for this command is:cluster [cluster name] RESOURCE [resource name] /option |
To use it in operation you should issue one of these commands:
cluster "SMSCluster" resource "OzekiNG" /offline cluster "SMSCluster" resource "OzekiNG" /online |
Version upgrade: To upgrade Ozeki NG SMS Gateway in your cluster to a new version in an active/passive configuration, you need to install the new version on the primary node only. The installation will update all files on the shared storage. The service registration of the old version (on the passive node) will work for the new version as well.
Changing service account: In some scenarios, for example in an SQL to SMS gateway configuration, you might need to change the service account of the OzekiNG service. This might be requested by your database administrator to meet database login policy requirements. Please note, that if you try to change service account information, such as the account name or the password, while OZEKI NG SMS Gateway is clustered, the service cannot start when you try to bring the cluster group online. In this scenario, you may have to manually remove Ozeki NG SMS Gateway completely from both nodes, and then reinstall SQL Server.
Alternative clustering technologies
An alternative to the introduced clustering solution can be created using Vinca's Co-StandbyServer, that is available at http://www.vinca.com/products/sbsnt/ntco_ds.html, you can also use Vinca's Octopus (http://www.legato.com/Products/octopus.html), or you can go for Network Specialists' Double Take (http://www.nsisoftware.com/main/pages/Products/DTspec.html). For shared storage solutions, you may NCR's LifeKeeper (http://www3.ncr.com/nt/lifekeeper.htm) or Veritas FirstWatch (http://www.veritas.com/product-info/fw/index.htm) and we should also mention Marathon's Endurance 4000 (http://www.marathontechnologies.com/).
References
Microsoft Cluster Service Installation Resourceshttp://support.microsoft.com/kb/259267
Step by step installation guide for setting up a cluster
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Bb727114.aspx
Setting up a windows server 2003 cluster in Microsoft Virtual Server 2005
Setting-Up-A-Windows-Server-2003-Cluster-in-VS2005-Part1.pdf
Setting-Up-A-Windows-Server-2003-Cluster-in-VS2005-Part2.pdf
