Premium-rate SMS services
Premium rate SMS messages allow you to monetize your content. Mobile service providers often allow 3rd party content providers to create mobile services using premium rate SMS messages. These services may be stock exchange rates, games for prizes, tests, data services etc. Premium rate SMS messages make it possible to collect money from users of these value-added services. Since the amount of money collected is rather small, these services are often referred to as micropayment services.
What are premium SMS services?
Premium SMS is a billing method for buying mobile content and other goods/services.
Enable premium rate SMS payments to monetize content, goods, and services for customers.
What can you sell with premium SMS services
Today's most popular premium SMS services are stock exchange rates, downloadable games, music and information services (e.g.: weather, news, programs).
- Interactive Services: Interactive media services, TV show voting and donations
- In-App Payments: Provide payment options for mobile app users to buy in-app content, including extra content, additional app features, or subscriptions, using premium SMS messages.
- Ticketing: Allows ticket purchases for transportation, car parking, or events with premium SMS.
- Marketing: Competitions, promotions or marketing games for customers
How does the premium SMS service work?
The person who would like to use the premium rate service sends an SMS message to a premium rate phone number. When the SMS arrives in the Short Message Service Centre (SMSC) of the service provider, the SMSC recognizes that the destination phone number belongs to a "content server". As the next step, the message is transferred to a content provider's server over a TCP/IP connection. The content provider's server receives the SMS messages and generates a response SMS according to the implemented business logic. The response SMS travels back to the SMSC for transmission over TCP/IP, just as the request SMS was transferred to the content server. In most situations, the content server and the SMSC communicate over the Internet (Figure 1).
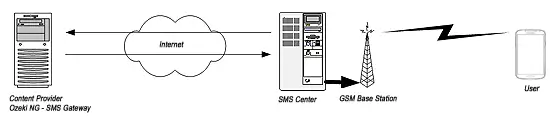
The benefits of Premium SMS
- Fast and easy payment system with a single SMS
- Ideal for micropayments
- The purchasing process is automatic, and no technical work required
- Real-time reporting
- Instant Payment
- Premium SMS is compatible with all mobile devices and operators
- Available worldwide
- Compatible with all mobile devices, operating systems (Android and iPhone), and service providers.
The business logic of the content server can be simple or complex. One of the most common solutions is based on content interpretation. A simple algorithm compares the incoming message text to a set of keywords, and generates a response based on the keyword. Another common application collects the phone numbers of the received messages and uses these phone numbers to provide periodic information services, such as traffic report or weather report every morning. There are many other types of solutions, as well. One thing they have in common is that in every case a reply SMS message must be sent back to acknowledge the service request within a limited response time (usually in 2 minutes).
Some useful information:
- Premium rate SMS prices cannot be chosen freely. In most cases the content provider must select a price offered by the GSM service provider.
- One premium rate phone number can run several services but can only operate with one price.
- It is not possible to send/receive premium rate SMS messages using SIM cards of foreign countries. It means that there is no such thing as premium rate roaming.
- When creating a solution, it is important to check if premium rate messages can be sent to our service from every GSM network in the country. Sometimes it is necessary to sign a contract with all GSM providers independently.
- Premium rate SMS services cannot be operated using a GSM phone attached to the PC with a phone-to-pc data cable.
- Premium rate SMS service phone numbers are often different from normal price phone numbers. They often use a special prefix, such as 06 90.
- If there is no response to the premium rate SMS, the Mobile Service provider does not charge the customer.
What is the difference between normal-priced SMS and Premium SMS?
Premium SMS is priced higher due to the added micro service provided by the premium SMS number owner. Premium SMS serves as a micropayment method.
More information
