GSM Modem Connectivity
Video tutorial: How to configure a GSM phone or GSM modem connection
In this chapter you can learn how to install and configure GSM modem connectivity for SMS messaging using the Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway software.
Introduction
If you plan to send and receive fewer than 15 000 SMS messages per day, you can use a suitable GSM device (phone or modem) attached to your computer with a phone-to-PC data cable. For information about suitable phones, check out the Supported Phones page. The GSM device has to be equipped with a SIM card that charges (preferably) low rates for SMS messages.
With this setup you can use a computer program such as Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway to send and receive SMS messages. In this case, the software uses the attached device to communicate with the GSM network. If a message is sent out by the gateway running on the computer, it is first sent to the attached GSM device. Then the GSM device transmits it to the SMS Centre (SMSC) of the GSM service provider, using a wireless link (Figure 1).
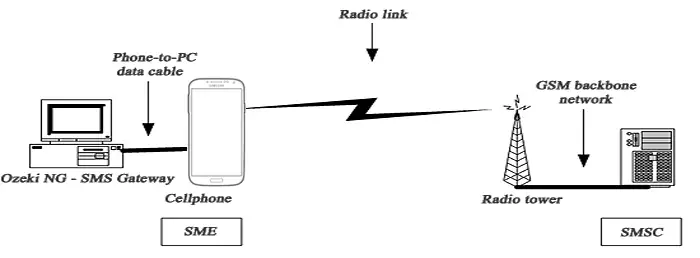
When a message is received, the GSM device stores the message in its memory or on the SIM card and sends a notification to Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway. When the program receives this notification, it retrieves (reads) the message from the respective memory cell, and then deletes the message from the device to make room for the next incoming message.
The advantage of using a cellular modem is that you do not need Internet connection for SMS messaging. Sending an SMS message using a cell phone takes about 5-6 seconds. Receiving takes about the same time. Good software, such as Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway allows you to attach more than one device to your PC and to use them simultaneously to increase capacity.
The best option to connect a phone to the PC is to use a standard RS232 serial cable. To find out more about it, check out the RS232 Serial Cable and Industrial Modems page. USB cables, InfraRed and Bluetooth connections are not as reliable. For information about attaching the GSM device with a USB cable, visit the USB Cable page.
Configuration of the GSM modem connectivity
When you have installed a GSM modem driver on your computer, you can start to install and configure the GSM modem connectivity.
You can install and configure this connection using the graphical user interface of Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway. To start the installation, click the Add button in the top right-hand corner of the Service providers panel on the left of the Management Console interface. (To find out how to open this interface, check out the QuickStart Guide.)
You can also add a service provider connection by clicking the Add service provider item in the Service providers menu. (To find out more about the menu, visit the Menu page.)
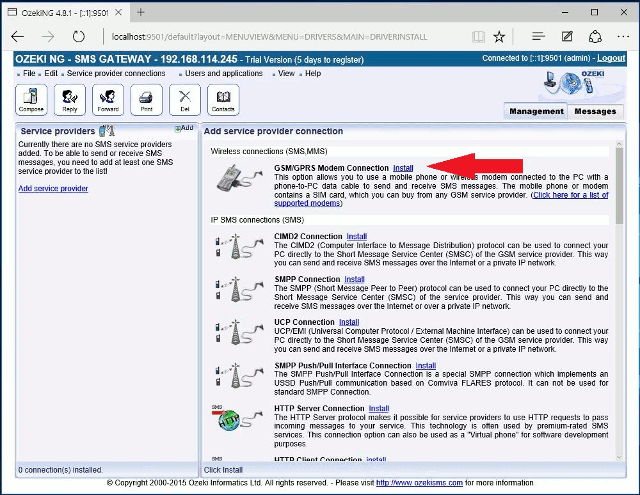
After you have clicked one of these, the Add service provider panel will show up on the right of the interface. The panel contains a list of protocols you can install and use for communication with an SMS service provider.
To select the GSM Modem protocol, click the Install link in the respective entry in the list (Figure 2).
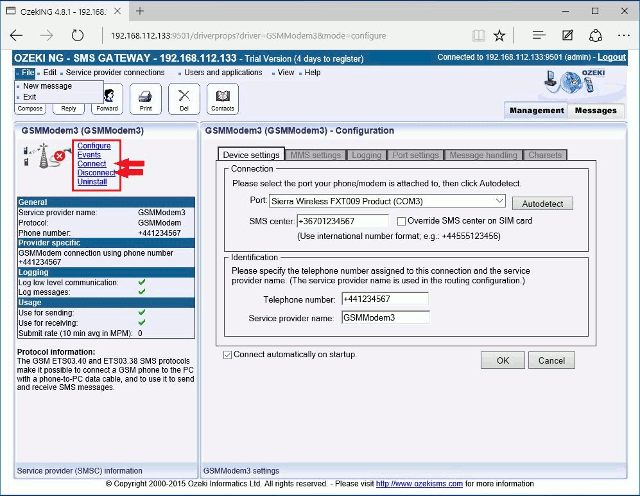
When you have installed the GSM Modem protocol, the Configuration panel will show up on the right of the interface. The first tab of the panel is the Device settings tab, which consists of a Connection and an Identification section (Figure 3).
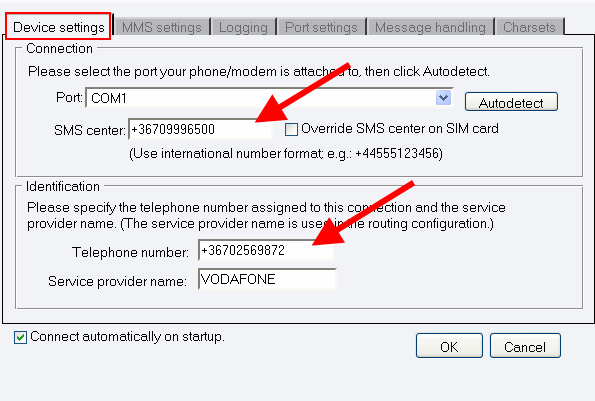
In the Modem or Port dropdown menu in the Connection section, select your GSM modem or the COM port your device is attached to.
In the SMS centre edit box, specify the phone number of the SMS centre of the GSM service provider you connect to. This address is provided by your GSM service provider. Some SMSC addresses are listed in this documentation. If you do not know the service centre address of your GSM service provider, you can check out Appendix C - SMS Service Centre Addresses.
In the Identification section, specify the telephone number assigned to this connection (the phone number of your GSM device) and the service provider name in the respective edit boxes.
Note that the phone number to be specified in the Telephone number edit box is a mandatory value. If you leave the edit box blank, the sending will be unsuccessful. Please also note that telephone numbers need to be provided in international format.
To facilitate identification and to avoid confusion, you should name the connection after the GSM service provider. E.g., if you have set up a GSM Modem connection with Vodafone, it is advisable to name it "Vodafone". Also, note that different connections should be given different names. If you have different connections from the same service provider, you can use different but similar names for them, e.g.: "Vodafone1", "Vodafone2" (or something of the like). However, some load balancing solutions require an identical name for different connections. For details, visit the Load Balancing and the Load Balancing for SMPP v3.3 page.
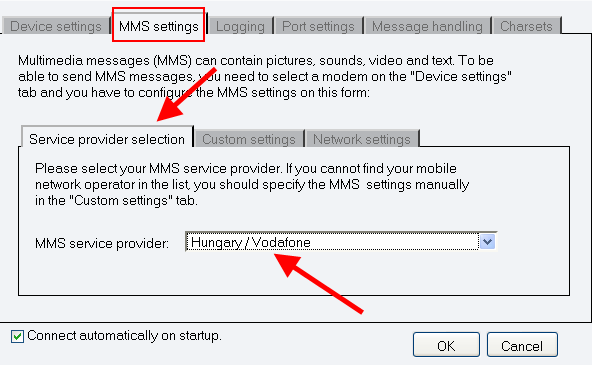
After you have selected a modem or port on "Device settings" tab, you can configure MMS settings if you wish to send MMS messages. Click on MMS settings tab. Select "Service provider selection" tab to select a service provider (Figure 4). If you cannot find your mobile network operator in the list, you should specify the MMS settings manually in the "Custom settings" tab (specify "GPRS APN", "MMSC URL", and the gateway to send MMS messages). Finally, on "Network settings" tab you can specify the GPRS connection settings.
To configure logging, click on Logging tab in Configuration panel.
The tab has a Logging and a Log file settings section. Here, you can choose whether to make the program write log entries about sent and received messages in human readable format and/or log low level communication. Choosing the latter option will make the program produce logfiles containing binary codes representing the communication data.
You should check at least the Log sent and received messages in human readable format checkbox, as logfiles can be useful in debugging communication problems (Figure 5).
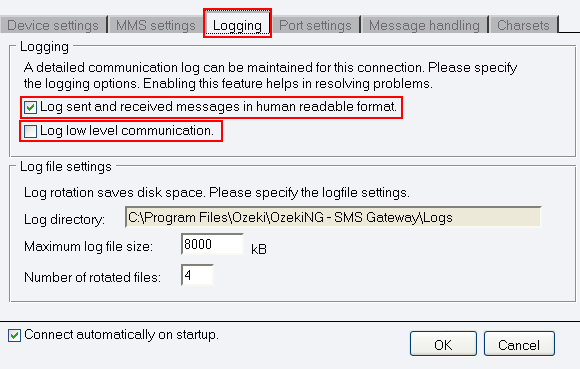
In the Log file settings section of the tab, you can make specifications for the size and the number of available logfiles.
Log rotation saves disk space, as it ensures that older (and probably no longer needed) logfiles will be automatically deleted from the log directory, which is specified in the Log directory text box. By default, the access path to the logfiles is: C:\Program Files\Ozeki\OzekiNG - SMS Gateway\Logs
In the Maximum log file size text box, you can specify the maximum size of a logfile. Once this size is reached, a new logfile will be created. Specify the number of kilobytes for the size of a logfile by entering a positive whole number. By default, the maximum logfile size is 8000 kB.
In the Number of rotated files text box, specify the maximum number of rotated logfiles that are saved. Specify this number by entering a positive whole number. By default, the number of logfiles that are saved is 4 (see Figure 5 above).
If you are content with the default specifications, leave the text boxes unchanged.
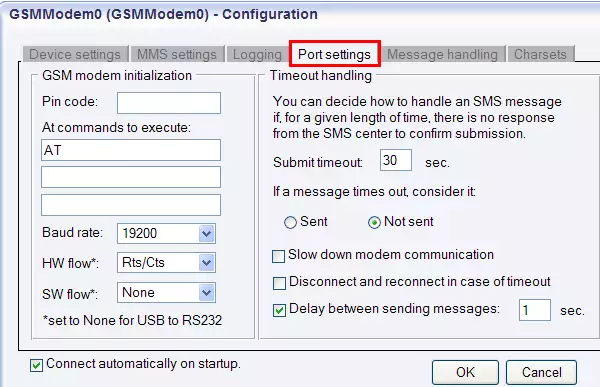
In the Port settings tab, you can modify the GSM modem initialization and specify the timeout handling commands.
In the Submit timeout edit box you can specify the maximum waiting time for an SMS Centre response confirming that your message has been successfully submitted. Successful submission means that the SMS Centre has accepted the message for delivery. You can specify the waiting time by giving the number of seconds in numerical characters representing any positive whole number. If you are content with the default specification (30 seconds), leave this edit box unchanged.
You can choose how to consider a message you have sent if there is no response from the SMS Centre after the specified length of time. Select one of the three radio buttons. Select Sent to consider a message sent even if there is no response from the SMS Centre. Select Not sent to consider a message not sent if there is no response from the SMS Centre.
Then you can enable the following options: Slow down modem communication, Delay between sending messages (you can specify the exact time), Disconnect and reconnect in case of timeout (Figure 6).
In the Message handling tab, you can make settings related to retrieving incoming messages and sending outgoing messages (Figure 7).
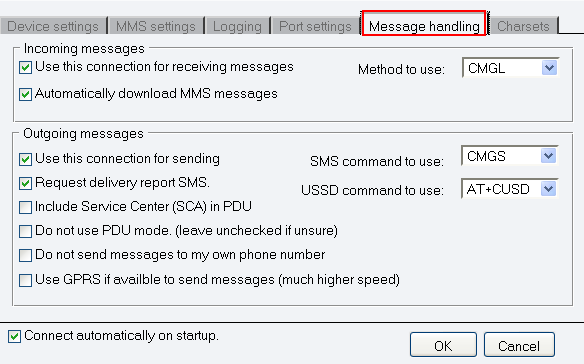
In Incoming messages section, you can enable two check boxes: Use this connection for receiving messages and Automatically download MMS messages.
In the Method to use to read incoming SMS dropdown menu, you can select which method to use to read incoming messages: CMT, CMGL or CMGR.
Use the CMT method to make the GSM device send a notification about incoming messages.
Use the CMGL method to request the list of incoming messages.
Use the CMGR method to read the content of memory cells one at a time.
The latest standard is CMT.
In Outgoing messages section, you can enable or disable the following options: enable Use this connection for sending to be able to send out messages; and Request delivery report SMS if you wish to receive delivery reports via SMS about the status of your sent messages. Include Service Centre (SCA) in PDU and Do not use PDU mode (leave unchecked if unsure): SMS messages can be received in two ways: by text mode and by protocol description unit (PDU) mode. If PDU mode is used, any encoding can be implemented. If you check Do not send messages to my own phone number you can prevent the program from sending SMS messages to yourself, i.e. to the phone number of your SIM card. You can also check Use GPRS if available to send messages option as it ensures much higher speed.
After you have checked the boxes, you wish to use, specify SMS command to use. You can select CMGS or CMGT. Then select ATDT or AT+CUSD options for USSD command to use.
The Configuration panel for service provider connections contains a Connect automatically on startup checkbox (in the bottom left-hand corner). If it is checked, Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway will automatically initiate a connection with the SMS Centre when the program has started. If this checkbox is not checked, the connection has to be initiated manually.
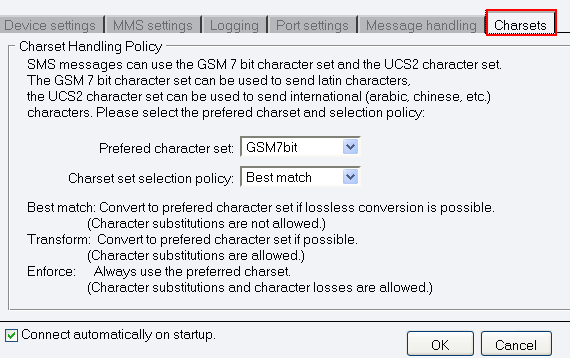
In Charset tab you can specify the character set handling policy. To Preferred character set you can select UCS2 or GSM7bit. SMS messages can use the GSM 7-bit character set and the UCS2 character set. The GSM 7-bit character set can be used to send Latin characters, the UCS2 character set can be used to send international (Arabic, Chinese, etc.) characters.
In Charset set selection policy line you can select one of the following options:
Best match: Convert to preferred character set if lossless conversion is possible. (Character substitutions are not allowed.)
Transform: Convert to preferred character set if possible. (Character substitutions are allowed.)
Enforce: Always use the preferred charset. (Character substitutions and character losses are allowed.) (Figure 8).
You can connect a service provider connection by clicking the Connect link in the panel of the service provider connection. To disconnect a service provider connection, click to the Disconnect (Figure 9).
You can open the panel of a service provider connection by clicking the name of the service provider connection in the Service providers panel in the Management Console.
The panel of a service provider connection consists of three sections.
In the upper section you can find the name of the service provider connection (with the name of its protocol in brackets).
You can see an icon showing if the service provider connection is connected. If it is not, the icon is marked with an "x".
To the right of the icon, you can find links to perform different operations.
- Configure: to configure or modify the configuration of an installed service provider connection. Clicking this link will take you back to the Configuration panel.
- Events: to view the logging of the latest server events related to the service provider connection. Clicking it will bring up the Events panel containing the logging of the latest server events.
- Connect: to connect the service provider connection with the SMS Centre.
- Disconnect: to disconnect the service provider connection from the SMS Centre.
- Uninstall: to uninstall the service provider connection.
In the middle section of the panel, you can see some of the most important configuration information. The options that have been (re)activated during the configuration are marked with a tick. The options that have not been activated or those that have been deactivated during the configuration are marked with an "x".
In the lower section of the panel of the service provider connection you can read some information about its protocol.
FAQs
Can I use Ozeki NG and Ozeki Message Server 6 on the same computer with the same GSM modem at the same time?
When it comes to using Ozeki NG and Ozeki Message Server 6 on the same computer
with the same GSM modem, there are some considerations:
A GSM modem can only be accessed exclusively.
This means that if you connect to it using one application (e.g., Ozeki NG), it
becomes locked and cannot be accessed by another application (e.g., Ozeki Message Server 6).
To enable both software applications to send SMS messages, follow this approach:
Configure the GSM Modem in Ozeki NG.
Use Ozeki NG as an IP SMS service provider for Ozeki Message Server 6.
Ozeki NG has a built-in SMSC (Short Message Service Centre) that can connect clients using the SMPP protocol.
To set this up, create an SMPP user account in Ozeki NG.
From Ozeki Message Server 6 (or any other SMS software), connect to the built-in SMSC of Ozeki NG using the following connection information:
- IP: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 9500
- SMPP Username and SMPP Password: Specify these when creating the SMPP user in Ozeki NG.
Can I use Ozeki NG and Ozeki Message Server 6 on the same computer with two modems?
Yes, you can. If you have Ozeki NG assigned to one modem and Ozeki Message Server 6 assigned to another modem on the same computer, both programs can coexist and function independently. The two modems can be different models or even identical ones.
Will the software run on a Virtual Machine, such as VMWare, Microsoft Virtual PC?
Certainly! Ozeki NG SMS Gateway is compatible with virtual machines such as VMWare and Microsoft Virtual PC. If you use an IP SMS connection, the SMS Gateway will work seamlessly within the virtual environment. IP SMS connections rely on network communication, which is well-supported in virtual machines. If you use a USB GSM modem, you might encounter challenges when configuring it within a virtual machine. Ensure that the USB modem driver supports virtualization. Some USB modems may not work as expected due to limitations or compatibility issues. Keep in mind that the performance of virtual machines can be suboptimal compared to physical hardware. Factors such as CPU, memory, and I/O affect performance. Test thoroughly to ensure satisfactory performance for your specific use case.
Which phone models/GSM modems do you recommend?
When choosing a GSM modem for your SMS solution, consider the following recommendations and features:
We recommend the following GSM modems for building a reliable SMS solution:
- Wavecom Fastrack MB1306B
- Siemens MC35
- Siemens TC65
- Maestro 100
Ensure the chosen phone model or GSM modem has the following features:
- Built-in Modem: The device should have a built-in GSM modem.
- Data Cable: It should support a USB or RS232 data cable for connectivity.
- GSM 7.05 Standard: The phone should support the GSM 7.05 standard for SMS messaging.
- Avoid Symbian OS: Phones with the Symbian OS may have issues with SMS receiving.
Consider industrial GSM modems like:
- Siemens MC35
- Wavecom Fastrack
- Maestro 20/100
These modems are stable, reliable, and suitable for professional applications. They can be connected to a PC using an RS232 cable.
Additional Notes:
- Siemens and SonyEricsson handsets also work well.
- Avoid Nokia models and PCMCIA modems based on our experience.
- Symbian-based telephones cannot be used to receive SMS messages.
